In contemporary electronics manufacturing, Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA) technology stands as the quintessential framework for the production of an extensive spectrum of electronic devices that have seamlessly integrated into modern societal infrastructure. From ubiquitous gadgets like smartphones and computers to critical systems in medical and automotive domains, the omnipresence of PCBA technology underscores its pivotal role in shaping our technological landscape. A comprehensive comprehension of PCBA technology necessitates a profound understanding of its elemental constituents and the intricacies entailed in their amalgamation.

At its nucleus, PCBA technology encompasses the integration of electronic components onto a printed circuit board (PCB) to engender a functional electronic assembly. The PCB, functioning as the substratum, accommodates electronic components such as resistors, capacitors, integrated circuits, and connectors, interconnected via conductive pathways or "traces." These traces, predominantly composed of copper, delineate a network that facilitates the transmission of electrical signals and power among components, thereby enabling the coherent operation of the device.
A comprehensive comprehension of PCBA technology mandates an in-depth insight into the components it employs. Resistors assume a pivotal role in regulating the flow of electrical current within the circuit, while capacitors serve as reservoirs for electrical energy, effectuating controlled release as necessitated. Integrated circuits, colloquially known as microchips or ICs, serve as the computational nucleus of electronic devices, executing a gamut of functions spanning from data processing to signal amplification and control logic. Conversely, connectors facilitate both physical and electrical interfacing between the PCB and external peripherals, facilitating seamless input/output (I/O) operations.
PCBA technology encompasses a meticulously orchestrated series of processes, culminating in the coherent assembly of electronic components onto PCBs, ensuring the reliability, functionality, and quality of the final electronic assembly.
PCB Fabrication
The inception of the journey lies in PCB fabrication, wherein the conceptual circuit layout metamorphoses into physical PCBs through a sequence of manufacturing processes. This entails substrate material selection, circuit layout design, etching, drilling, solder mask application, and surface finishing. Precision and accuracy in PCB fabrication are paramount, as any aberrations or inconsistencies may detrimentally affect the performance and reliability of the final electronic assembly.
Component Placement
Component placement assumes a pivotal role in PCBA technology, wherein electronic components are meticulously positioned on the PCB in accordance with the circuit design. This process may be executed manually by proficient technicians or automated via advanced pick-and-place machinery furnished with vision systems for precise component alignment. Prudent component placement is imperative to ensure optimal electrical performance and reliability of the final electronic assembly.
Soldering
Soldering constitutes the process of permanently affixing electronic components to the PCB utilizing solder—an amalgam of fusible metals boasting a low melting point. During soldering, the solder is subjected to heat, enabling it to liquefy and engender a metallurgical bond between the component leads and the PCB pads. This bond not only ensures electrical conductivity but also furnishes mechanical strength, thereby fortifying the components in situ and engendering dependable electrical connections.
Inspection
Inspection emerges as a pivotal juncture in the PCBA process, aimed at discerning and rectifying any imperfections or anomalies that might compromise the quality and functionality of the electronic assembly. Diverse inspection techniques, inclusive of visual inspection, automated optical inspection (AOI), and X-ray inspection, are employed to meticulously scrutinize solder joints, component placement, and overall PCB assembly integrity. Timely and exhaustive inspection is indispensable to guarantee the reliability and performance of the end product.
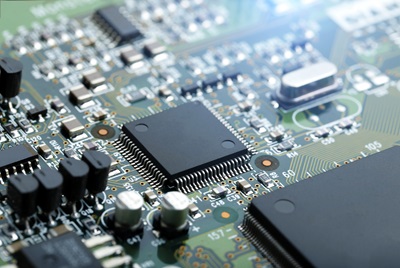
A comprehensive grasp of the indispensable components and processes constituting PCBA technology is imperative for individuals involved in the design, manufacturing, or maintenance of electronic devices. Ranging from resistors and capacitors to integrated circuits and connectors, each component assumes a pivotal role in delineating the functionality and performance of electronic assemblies. Likewise, the processes of PCB fabrication, component placement, soldering, and inspection are integral to the realization of functional and dependable electronic products. By delving into the intricacies of PCBA technology, one cultivates a profound appreciation for the nuanced interplay of components and processes underscoring modern electronics, thus fostering innovation and advancement in this perpetually evolving domain.
By continuing to use the site you agree to our privacy policy Terms and Conditions.