In our contemporary world, electronic devices reign supreme, seamlessly integrating into every aspect of our lives. Yet, beneath their sleek exteriors lies a fundamental component that powers their functionality: printed circuit board assemblies (PCBAs). This article delves into the intricacies of PCBAs, shedding light on their structure, manufacturing process, applications, and future trends.
PCBAs are comprised of two primary elements: the base material and copper traces. The base material, typically fiberglass or ceramic, provides structural integrity and electrical insulation. Copper traces, etched onto the base material using photolithography, form intricate pathways for electrical currents, facilitating communication between electronic components.
Moreover, PCBAs may incorporate additional components such as passive components (resistors, capacitors, inductors), active components (transistors, diodes, integrated circuits), and connectors, enhancing their functionality and versatility.
Design: Schematic diagrams are created, and circuit board layouts are generated to outline the configuration of the PCBA.
Fabrication: The base material is fabricated to precise specifications regarding thickness and shape.
Etching: Copper traces are etched onto the base material according to the predefined circuit design.
Solder Mask Application: A protective solder mask layer is applied to safeguard the copper traces from corrosion.
Component Placement: Electronic components are meticulously placed onto the board, adhering to the circuit layout.
Soldering: Components are soldered onto the board, establishing electrical connections.
Testing: Rigorous testing procedures are conducted to ensure the PCBA meets stringent performance specifications.
PCBAs find ubiquitous applications across diverse electronic products:
Computers: Facilitating connectivity between components such as CPUs, memory modules, and storage devices.
Smartphones: Enabling seamless integration of components like displays, cameras, and sensors.
Televisions: Connecting essential components including displays, tuners, and audio systems.
Appliances: Powering control functions in household appliances like refrigerators, washing machines, and microwave ovens.
Automation: Increasing adoption of automation technologies to enhance manufacturing efficiency and precision.
Green Technologies: Embracing eco-friendly practices to minimize the environmental footprint of PCBA manufacturing.
Continued Growth: Anticipating sustained expansion as the electronics industry burgeons, propelled by ongoing advancements in PCBA technology.
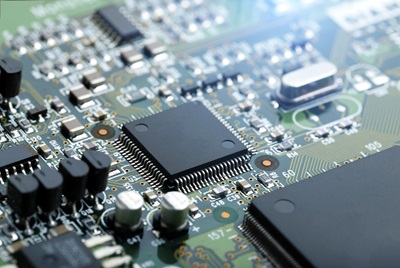
In essence, PCBAs serve as the backbone of electronic products, facilitating seamless functionality across various applications. As the PCBA industry embraces automation, green technologies, and ongoing innovation, it is poised for continued growth, reaffirming its indispensable role in powering the electronics revolution.
By continuing to use the site you agree to our privacy policy Terms and Conditions.